Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
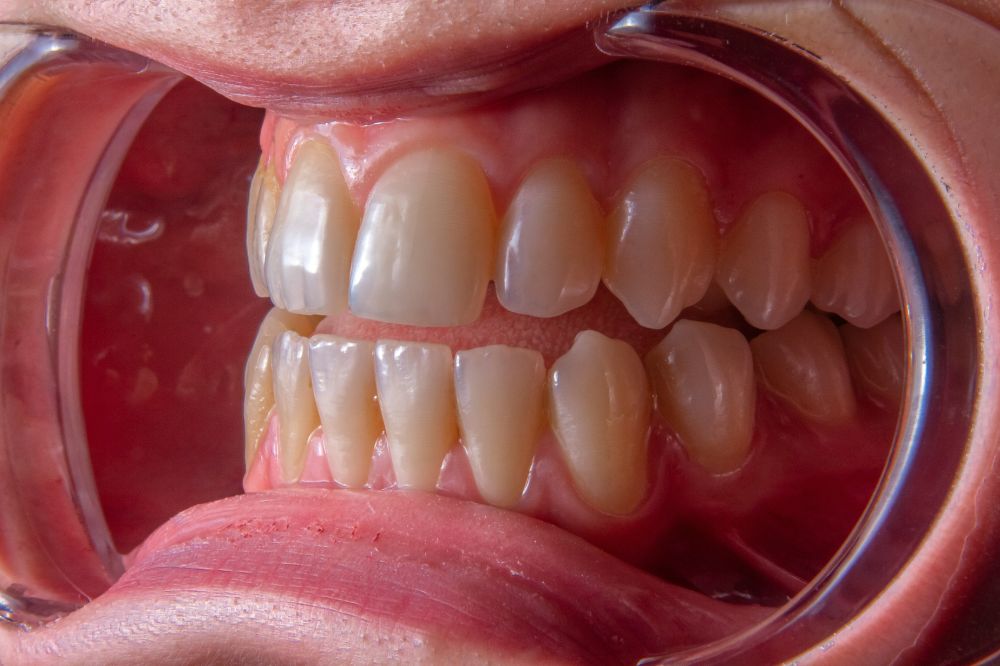
Receding gums are usually a sign of gum disease (including gingivitis and periodontitis ) and are typically not reversible. In extreme cases, you’ll need gum graft surgery to restore your receded gums. Over 50% of American adults experience some level of receding gums. Although poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gum recession, other causes include hormone changes and injuries to your teeth or gums.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
These are the most common symptoms that accompany receding gums:
- Swollen red gums
- Sensitive gums
- Bleeding gums, especially after brushing or flossing
- Longer tooth appearance, ability to see higher on your tooth
- Sensitivity to cold and hot foods
- Loose teeth
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Receding gums are most typically a symptom of early or advanced gum disease. Untreated gum disease can lead to serious whole-body health issues, such as tooth loss, heart disease, and lung infection. Can my teeth fall out if I have receding gums? Yes, if you have receding gums, there might eventually not be enough gum tissue to hold your tooth. One or more teeth can fall out if your gums recede too far.
Causes & Risk Factors
Why do gums recede? Gums recede because of bacteria buildup around your gums or because of injury to your gums. Here are all the causes and risk factors for receding gums:
- Poor dental hygiene
- Brushing your teeth too hard
- Dental plaque buildup
- Tartar buildup
- Gingivitis, periodontitis, or periodontal disease (all similar terms)
- Dental misalignment
- Injury to your gums, including from hard or sharp food
- Lip or tongue piercings
- Use of tobacco products
- Aging
- Family history of gum disease
- Hormonal changes
- Diabetes
- HIV/AIDS
Can Receding Gums Grow Back?
Receding gums can’t grow back. Once it’s gone, your gum tissue is gone for good. However, some treatments may stop or slow further gum recession.
Your periodontist needs to diagnose whether you actually have receding gums, discuss treatment options like gum grafting with you, and identify if bone grafting is necessary due to substantial bone loss.
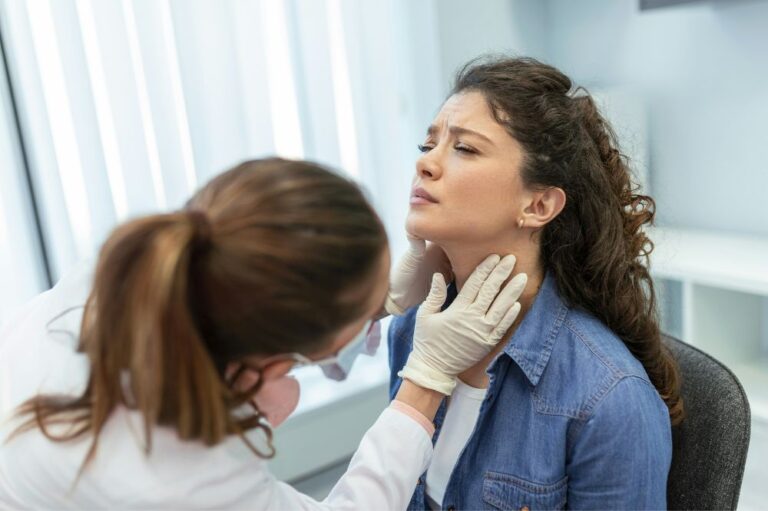
How Gum Recession Is Diagnosed
Your normal dentist can diagnose gum recession during your twice-yearly checkup. The dentist will calculate gingival recession for each tooth using a periodontal probe — a small painless ruler that measures gingival pocket depth. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research states that a normal gingival pocket ranges from 1 to 3 millimeters. Deeper than 1-3 mm means you have gum disease. Simply improving your oral care routine may solve the issue if you have mild gum recession.
But if the root of the tooth is exposed, you’ve got a serious dental problem. Exposed roots may lead to tooth sensitivity, tooth loss, and the spread of infection throughout the body. Bone loss is common near receding gums, so your dentist may order x-rays or further diagnostic tests. If you’ve got a severe enough case of gum disease, your dentist may refer you to a periodontist for more specialized treatment.
Schedule your appointment with Rejuvenation Dentistry today and start living your new life with a gleaming, all-natural smile!
How to Stop Receding Gums (Treatments)
Can a receding gum be fixed? Receding gums can be stopped but not reversed. In most cases, only surgery can restore your gum tissue.
Gum grafting surgery is traditionally the only treatment that can actually restore your gums by taking existing soft tissue in your mouth and grafting it to your tooth roots.
Other gum-healing treatment options can slow or stop the progression of receding gums:
- Better oral hygiene (not brushing too hard, flossing gently every day, etc.)
- Twice-yearly visits to your dentist
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning performed by a dental professional)
- Low-sugar diet (preferably rich in omega-3s, vitamins C and D, and fiber )
- Eucalyptus oil (or concentrated eucalyptus gum)
- Unsweetened green tea (for gum health and overall wellness )
- Ozone therapy (read more about the benefits of ozone therapy )
- CBD (to reduce pain and swelling)
- Antibiotics, to kill harmful bacteria
Surgery for Gum Recession
If receding gums are impacting your health or appearance, you and your healthcare provider can discuss the benefits of an oral surgery called “free gingival graft” or “gum grafting.” Gum surgery might sound scary, but it is safe and painless when your gums are adequately numbed.
Gum grafting surgery is a tremendous long-term treatment for receding gumsto avoid the damaging effects of gum recession. This surgery can also improve the appearance of your smile by restoring your natural gum line. Your dentist or doctor can refer you to a periodontist (gum specialist) who can perform the gum tissue graft.
During this surgery, a periodontist removes some tissue from the roof of your mouth or nearby healthy gum tissue. The removed tissue is attached to where your gums have receded. This procedure is simple, safe, common, quick (under an hour), and outpatient (you can leave after the procedure).
What Happens if You Don’t Treat Receding gums?
If you leave receding gums untreated, it can lead to the following health complications:
- Tooth loss
- Tooth mobility
- Bleeding gums
- Gingivitis, periodontitis, or advanced gum disease
- Change in your bite
- Pain while chewing
- Damage to the sur

Dr. Gerry Curatola
Dr. Gerry Curatola is a renowned biologic restorative dentist with more than 40 years of clinical practice experience. He studied neuroscience at Colgate University and attended dental school at the New York University (NYU) College of Dentistry where he now serves as Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor in the Department of Cariology and Comprehensive Care.

Dr. Gerry Curatola
Dr. Gerry Curatola is a renowned biologic restorative dentist with more than 40 years of clinical practice experience. He studied neuroscience at Colgate University and attended dental school at the New York University (NYU) College of Dentistry where he now serves as Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor in the Department of Cariology and Comprehensive Care.